Preparation Tris-Borate Buffer
This guide describes the preparation of Tris-Borate Buffer at a defined molarity for laboratory use.
The following content was generated by AI and has not been strictly verified; it may contain inaccuracies. All information in the BioCalculator App has been manually curated and carefully validated. You can download the App to view it.
Tris-Borate (TB) buffer is an electrophoresis buffer lacking EDTA, suitable for high-voltage DNA electrophoresis and rapid separation of small DNA fragments.
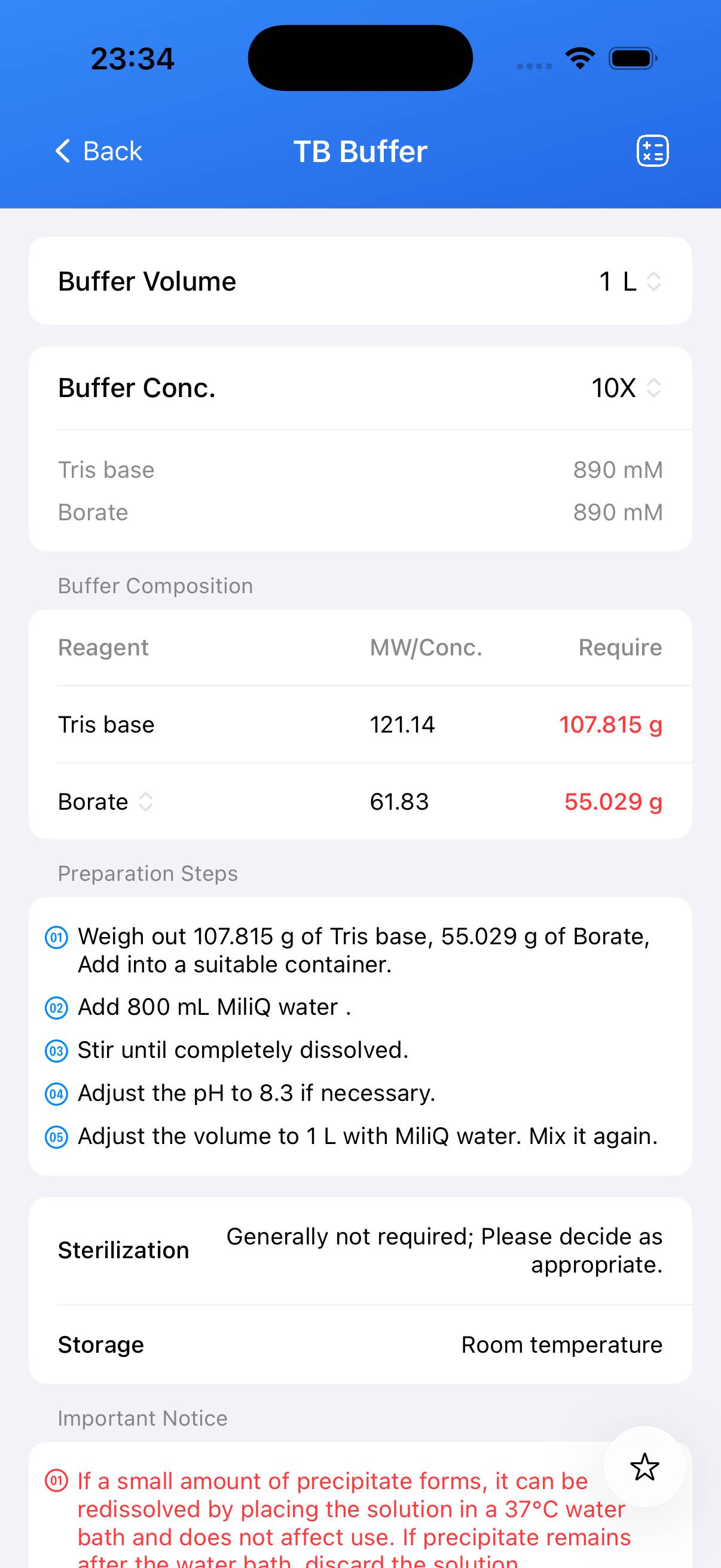
Tris-Borate (TB) Buffer – 1X Working Solution Composition
| Name | Formula | Concentration (1X) | CAS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tris base | C₄H₁₁NO₃ | 89 mM | 77-86-1 |
| Borate | H₃BO₃ | 89 mM | 10043-35-3 |
Applications of Tris-Borate (TB) Buffer
Tris-Borate buffer is commonly used in agarose gel electrophoresis for DNA analysis when EDTA is not desired. The absence of EDTA allows TB buffer to support high-voltage electrophoresis, enabling significantly faster separation (approximately three times faster than conventional buffers) and improved resolution, particularly for low-molecular-weight DNA fragments.
Preparation Tips, Sterilization, and Storage
- If a small amount of precipitate forms, it can be redissolved by placing the solution in a 37°C water bath and does not affect use. If precipitate remains after the water bath, discard the solution.
- EDTA-free TB electrophoresis buffer is suitable for high-voltage electrophoresis, enabling faster analysis and improved DNA resolution, especially for low-molecular-weight DNA.
- Sterilization: usually not required; select as needed.
- Storage: room temperature.