Preparation EDTA Stock Solution
This guide describes the preparation of EDTA Stock Solution at a defined molarity for laboratory use.
The following content was generated by AI and has not been strictly verified; it may contain inaccuracies. All information in the BioCalculator App has been manually curated and carefully validated. You can download the App to view it.
Stock Solution Preparation Guide – EDTA
EDTA (EthyleneDiamineTetraAcetic acid) is a polyamino carboxylic acid widely used in molecular biology as a chelating agent. It sequesters divalent and trivalent metal ions such as Zn2+, Ca2+, and Fe3+, which are required cofactors for many enzymes, including DNases.
Common Commercial Forms of EDTA
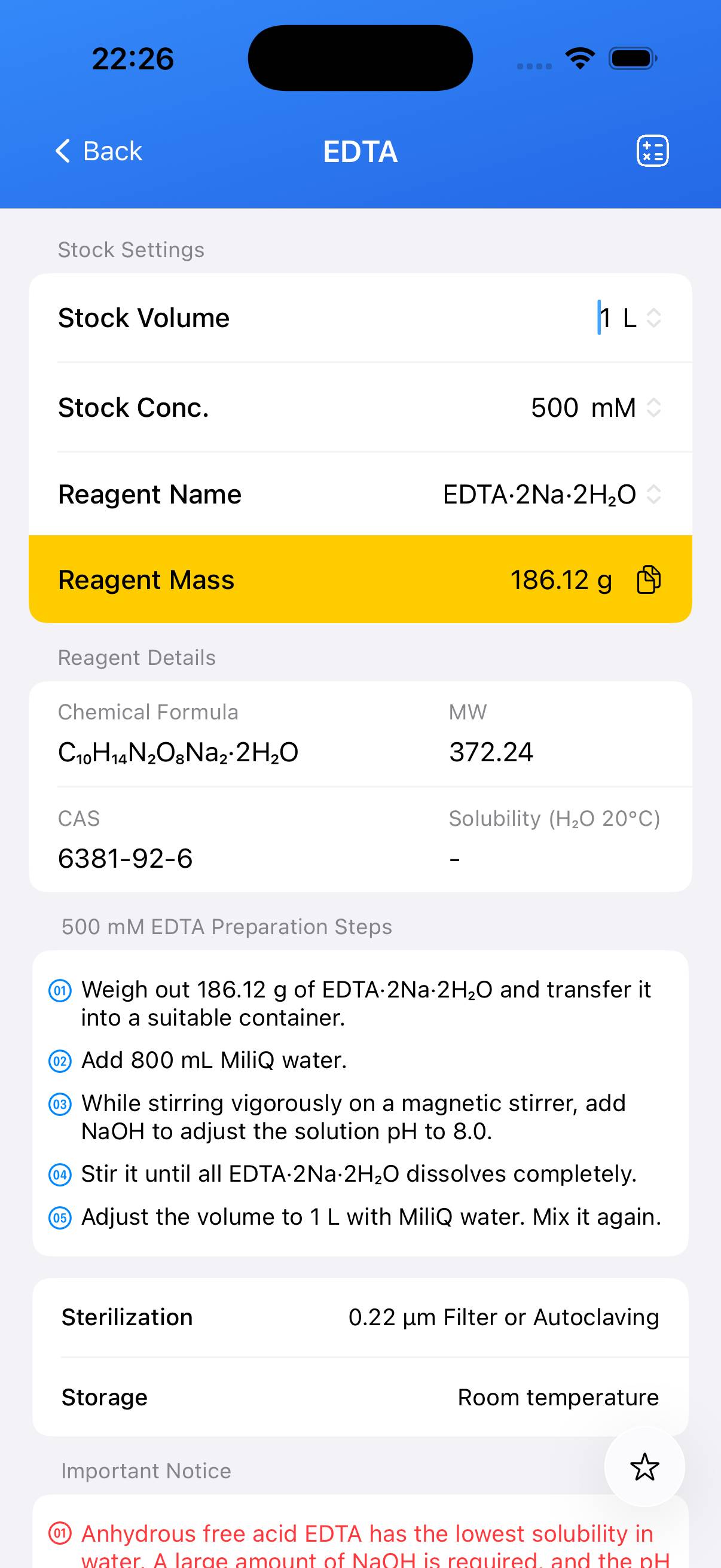
- Anhydrous EDTA (Free Acid) – CAS 60-00-4, MW 292.24
- Disodium EDTA Dihydrate (EDTA·2Na·2H₂O) – CAS 6381-92-6, MW 372.24
- Tetrasodium EDTA Tetrahydrate (EDTA·4Na·4H₂O) – CAS 13235-36-4, MW 452.23
Solubility and Experimental Considerations
- Anhydrous EDTA (Free Acid)
Has the lowest solubility in water. Dissolution requires the addition of a large amount of NaOH (approximately 3.1 molar equivalents) to raise the pH to 8.0. - Disodium EDTA Dihydrate
Has better solubility and is the most commonly used form for preparing 0.5 M EDTA stock solutions in molecular biology.next - Tetrasodium EDTA
Dissolves readily in water but results in a solution with pH > 10, making it unsuitable for most cell and molecular biology applications.
Available Reagents
| Name | Molecular Formula | MW | CAS |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA·2Na·2H₂O | C₁₀H₁₄N₂O₈Na₂·2H₂O | 372.24 | 6381-92-6 |
| EDTA (Free Acid) | C₁₀H₁₆N₂O₈ | 292.24 | 60-00-4 |
| EDTA·2Na | C₁₀H₁₄N₂O₈Na₂ | 336.21 | 139-33-3 |
| EDTA·4Na·2H₂O | C₁₀H₁₂N₂O₈Na₄·2H₂O | 416.20 | 10378-23-1 |
| EDTA·4Na·4H₂O | C₁₀H₁₂N₂O₈Na₄·4H₂O | 452.23 | 13235-36-4 |
Preview