Preparation Tris-EDTA Buffer
This guide describes the preparation of Tris-EDTA Buffer at a defined molarity for laboratory use.
The following content was generated by AI and has not been strictly verified; it may contain inaccuracies. All information in the BioCalculator App has been manually curated and carefully validated. You can download the App to view it.
Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer is a widely used buffering system for the storage and stabilization of DNA and RNA by maintaining pH and inhibiting nuclease activity.
Tris-EDTA (TE) Buffer – 1X Working Solution Composition
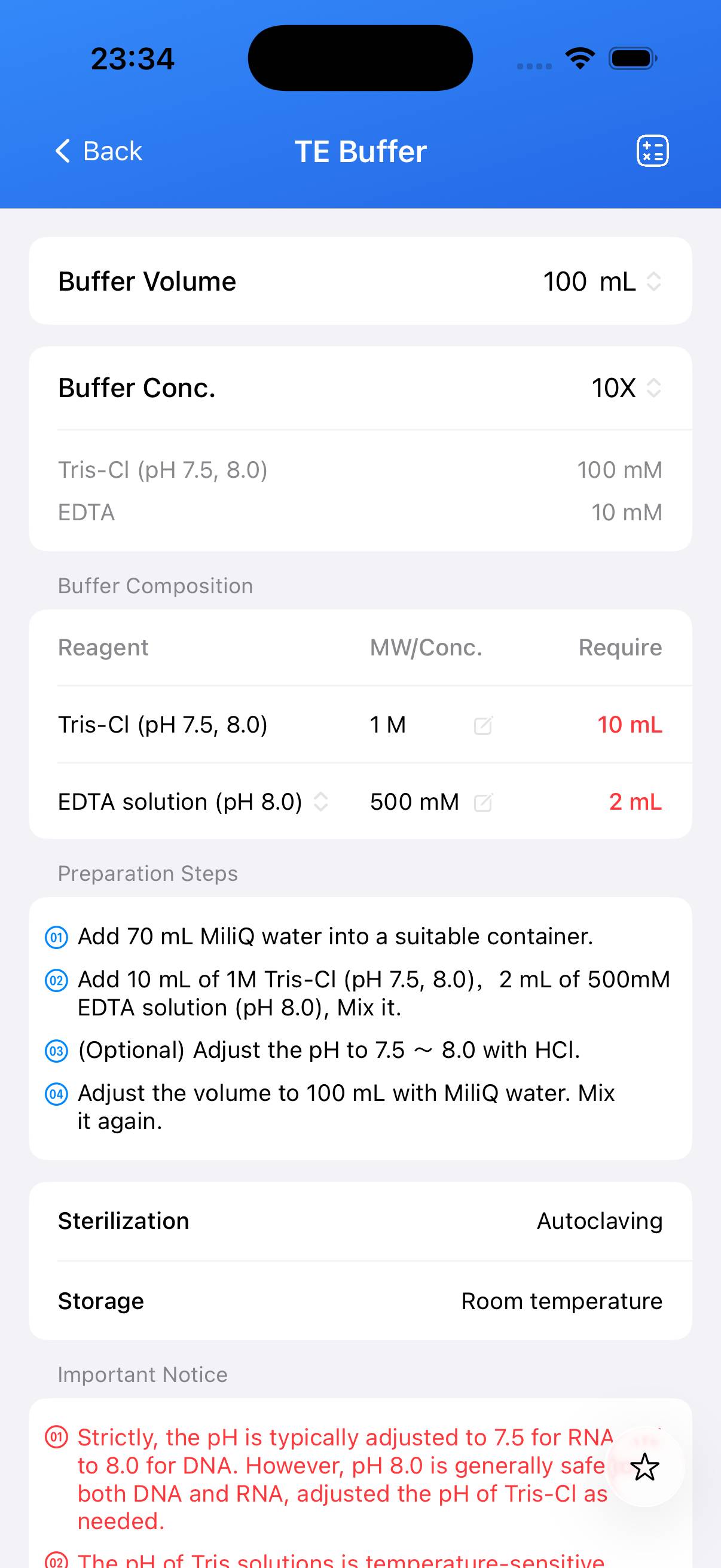
| Name | Formula | Concentration (1X) | CAS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tris-Cl (pH 7.5 or 8.0) | C₄H₁₁NO₃ | 10 mM | 77-86-1 |
| EDTA | C₁₀H₁₆N₂O₈ | 1 mM | 60-00-4 |
Applications of Tris-EDTA Buffer
Tris-EDTA buffer is primarily used for the storage, dilution, and stabilization of DNA and RNA. Tris maintains a stable pH environment, while EDTA chelates divalent metal ions such as Mg²⁺ and Ca²⁺, effectively inhibiting DNases and RNases. TE buffer is widely applied in molecular biology workflows including nucleic acid extraction, cloning, sequencing, and long-term DNA preservation.
Preparation Tips, Sterilization, and Storage
- Strictly, pH 7.5 is preferred for RNA, while pH 8.0 is commonly used for DNA; however, pH 8.0 is generally safe for both.
- The pH of Tris solutions is temperature-sensitive. Always adjust pH at room temperature.
- It is recommended to periodically verify the pH to ensure buffer stability.
- Note that sterilization by 0.2 μm filtration cannot guarantee complete removal or inactivation of all DNases.
- Genomic and plasmid DNA can be stored short-term in TE buffer at 4°C, or long-term at −20°C to −80°C. Avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles.
- EDTA (free acid) is extremely difficult to dissolve; preparing an EDTA stock solution in advance is recommended.
- Sterilization: autoclaving.
- Storage: room temperature.